In an increasingly digital business world, mobile applications and databases have become indispensable tools for collecting, processing, and utilizing valuable data. However, this treasure trove of information comes with a responsibility to protect the privacy of users.
Most of us outside the European Union's GDPR regulations and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States feel that our personal data is not in our control -- especially in the world of mobile apps. The above-mentioned regulations have introduced concepts like the right to be forgotten, data portability, and informed consent, making it imperative for developers to integrate these principles into their mobile apps and databases. At the same time, individuals have been granted greater control over their personal data. However, only in Europe and US.
In this article, we will explore the evolving landscape of data privacy rights, the challenges faced by developers, and innovative solutions that can help you ensure the protection of user data.
Challenges Faced by Developers
As a mobile app developer or owner, you still want to collect PII (personally identifiable information), but why risk trouble with government agencies when it’s a simple addition to protect users’ data. It is true that with great data collection power, comes great responsibility.
Developers encounter several challenges when implementing data privacy rights into mobile apps and databases. They include:
- Data Collection and Use Transparency
Ensuring that users are fully informed about the data being collected and how it will be used can be complex. Developers must provide clear and concise privacy policies and request consent in a user-friendly manner. But do all the users read them? That is a big question.
- Data Minimization
That means collecting only the necessary data for the app's functionality and nothing more. Striking the right balance between usability and data minimization is often a big task for both app developers and owners.
- Data Security and Protection
Protecting user data from breaches and unauthorized access is a constant concern. Developers need robust security measures, encryption protocols, and regular audits to maintain data integrity. But sometimes it is not enough.
- User Access and Control
Providing users with the ability to access, modify, or delete their data as per their preferences can be technically intricate but is fundamental to respecting their privacy rights and avoiding further conflicts. No one wants to ruin their reputation, right?
Modern solutions for Data Privacy
So, what are the innovative ways to overcome those challenges effectively?
Developers have at their disposal several of them:
1. Privacy by Design as the first step

Privacy by design is a fundamental concept here. It emphasizes the proactive integration of privacy and data protection principles into the design and development of systems, products, and processes from their very inception, rather than treating privacy as an afterthought or compliance requirement.
It has several characteristics:
- Proactive, Not Reactive - considering privacy and data protection issues at the earliest stages of designing and developing systems and technologies.
- Privacy as the Default Setting - users should not be required to take additional steps to protect their privacy; it should be the default situation.
- Full Functionality - users should be able to enjoy the full benefits and features of the technology without sacrificing their privacy.
- End-to-End Security - implementing robust security measures, encryption, and access controls to safeguard user data throughout its lifecycle.
- Visibility and Transparency - users should have clear and easy-to-understand information about how their data is being collected, processed, and used; privacy policies and notifications are transparent and accessible.
- User-Centric Approach - putting the interests and rights of individuals at the forefront. It empowers users with control over their own data, allowing them to make informed decisions about its use.
- Data Minimization - avoiding collecting excessive or irrelevant information that could potentially be misused or lead to privacy breaches
- Lifecycle Management - considering the entire data lifecycle, from collection to storage, processing, and disposal.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement - regularly monitoring and assessment of the effectiveness of privacy measures and making improvements fast when necessary.
- Legal and Ethical Compliance - keeping up to date with changing regulations and adapting the design.
Sounds promising, doesn’t it?
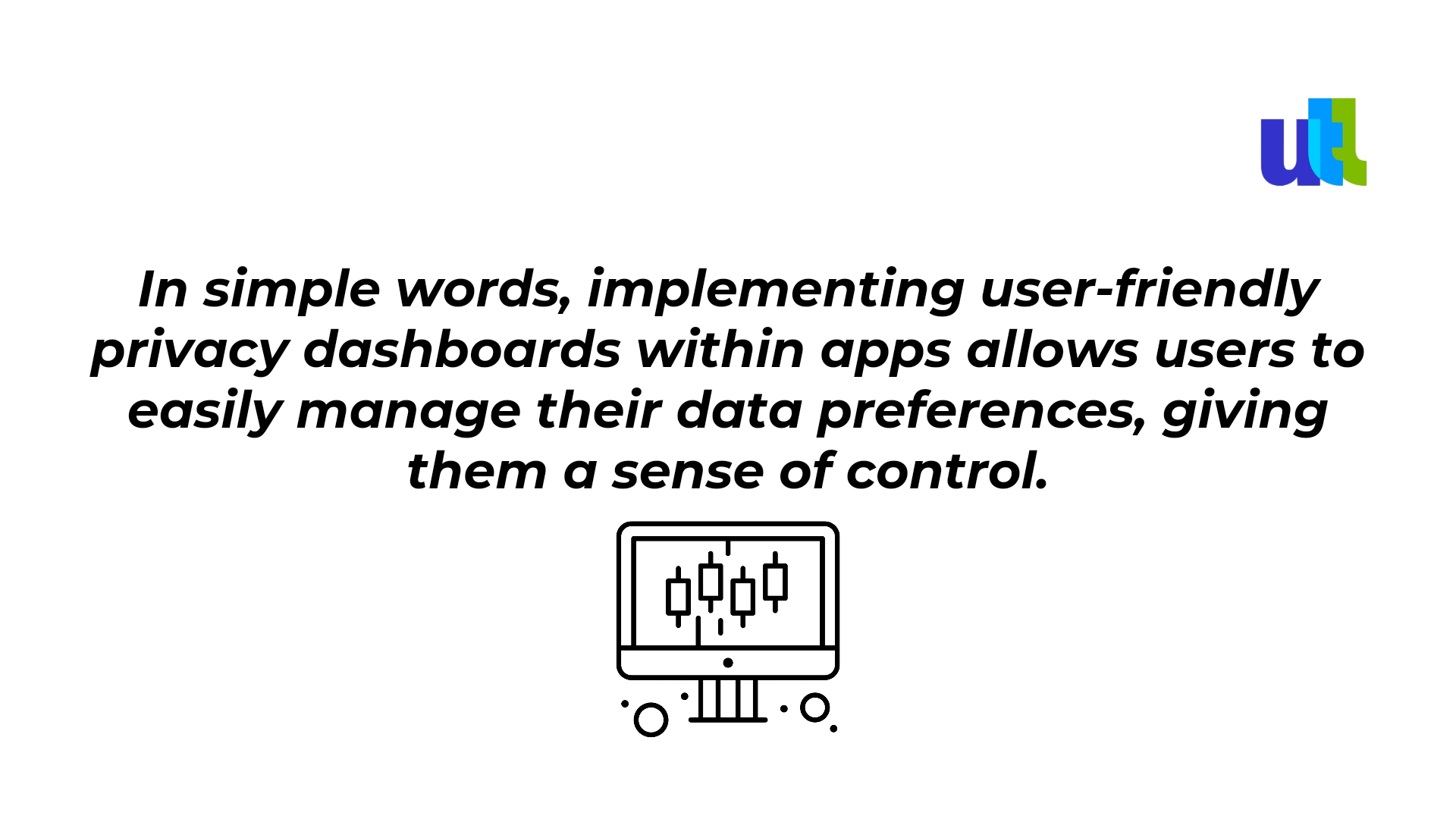
2. Privacy Dashboards for advanced control
As mobile apps often access a wide range of personal information, including location data, contacts, and more, privacy dashboards have been introduced. They provide users with an easy and accessible way to manage their data and privacy settings directly from their smartphones or tablets. Here are some of their key aspects:
- User Accessibility – they are designed to be user-friendly and easily accessible, typically integrated into the app's settings or preferences section.
- Data Collection Insights - including information about the specific data points being gathered, such as device information, usage statistics, or location data.
- Granular Controls – including options to toggle data collection on or off for specific features, as well as the ability to limit the frequency or extent of data sharing.
- Consent Management - being able to review and adjust their consent preferences through the dashboard helps users to feel safer while using the app.
- Data Deletion and Export - allowing users to delete their data stored within the app or request an export of their data for personal use or to switch to a different service.
- Privacy Policy Access – providing links to the app's privacy policy or terms of service and enabling users to review detailed information about data handling practices.
- Compliance with Regulations - allowing users to exercise their rights (like GDPR or CCPA).
- User Education - including educational elements to help users better understand their rights and the importance of data protection.
3. Blockchain Technology can help!
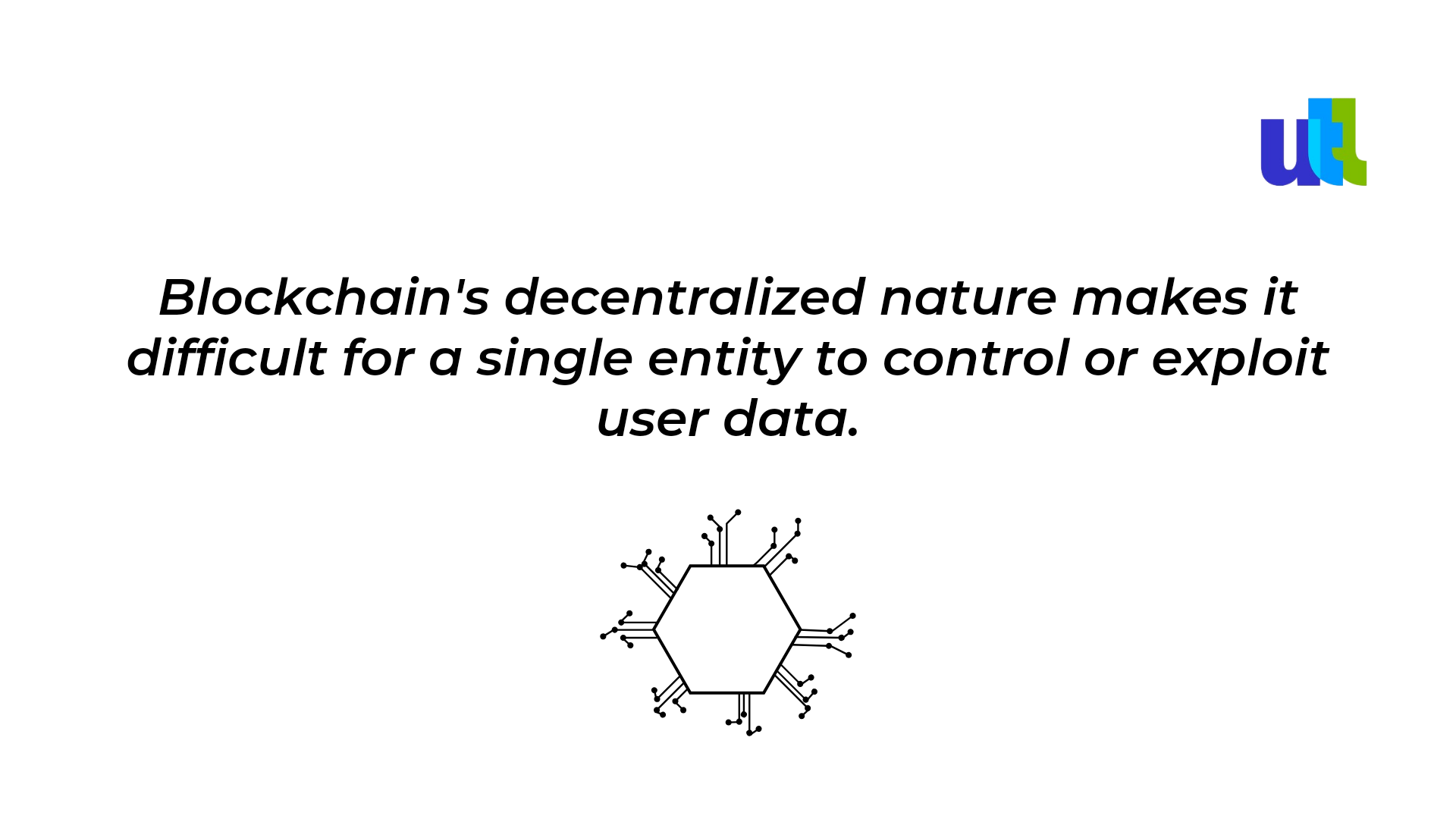
Blockchain, originally created as the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has evolved to have various applications beyond finance, including data privacy and security.
Here's how it can be employed to enhance data privacy in mobile apps:
- Decentralization and Data Control - making it difficult for a single entity to control or manipulate user data, since data is distributed across multiple nodes.
- Immutable Data – data becomes tamper-proof and immutable, and it is virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to alter or delete user information without consensus from the network.
- Data Ownership and Consent – introducing greater ownership and control over users’ data.
- Data Transparency - aligning with principles of data privacy and building trust.
- Data Portability – promoting data portability and interoperability while maintaining user control.
- Secure Identity Verification - offering a secure and decentralized way to verify user identities without exposing sensitive personal information.
- Compliance with Regulations – again, complying with data privacy regulations like GDPR by providing a robust framework for tracking and managing user consent and data access.
- Smart Contracts - self-executing agreements with predefined rules and conditions help automate the process.
- Anonymization and Pseudonymization - maintaining functionality while reducing the risk of privacy breaches.
However, the suitability of blockchain for a specific app depends on its use case and the nature of the data being handled.
4. Regular Auditing and Compliance Checks just to be sure!
Regular auditing and compliance checks should be an ongoing practice throughout the app's lifecycle, from development to deployment and maintenance.
These processes help ensure that mobile apps adhere to best practices, industry standards, and relevant regulations to protect user data. Here's a deeper look at their benefits:
Identification of Vulnerabilities - identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the app's design, code, and data handling processes.
Regular Updates - the app's update and patch management to keep the app compliant with evolving privacy regulations.
Third-Party Integrations – checking that these integrations do not compromise user data security or privacy.
Incident Response Planning - examining an app's incident response plan and, thus, mitigating their impact.
Documentation and Record-Keeping - demonstrating adherence to regulations in case of regulatory inquiries or legal disputes.
In general, they help ensure that the app remains secure, privacy-friendly, and compliant with changing regulations, ultimately fostering trust among users and protecting sensitive data.
To conclude
The journey to implementing data privacy rights in mobile apps and databases is a complex one. However, it's a must in today's data-driven world.
By embracing innovative solutions and making privacy a priority, we can ensure that the digital landscape becomes a safer, more respectful space for user data. Ultimately, empowering users with control over their personal information is not just a legal obligation but more of a moral imperative in the age of data.
For free consultation on mobile apps and databases, click here.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
View the full presentation:
< /p>
WRITTEN BY
Sofia Kutko
2023-10-11