In the intricate web of modern IT ecosystems, the supply chain represents a new battleground for cybersecurity.
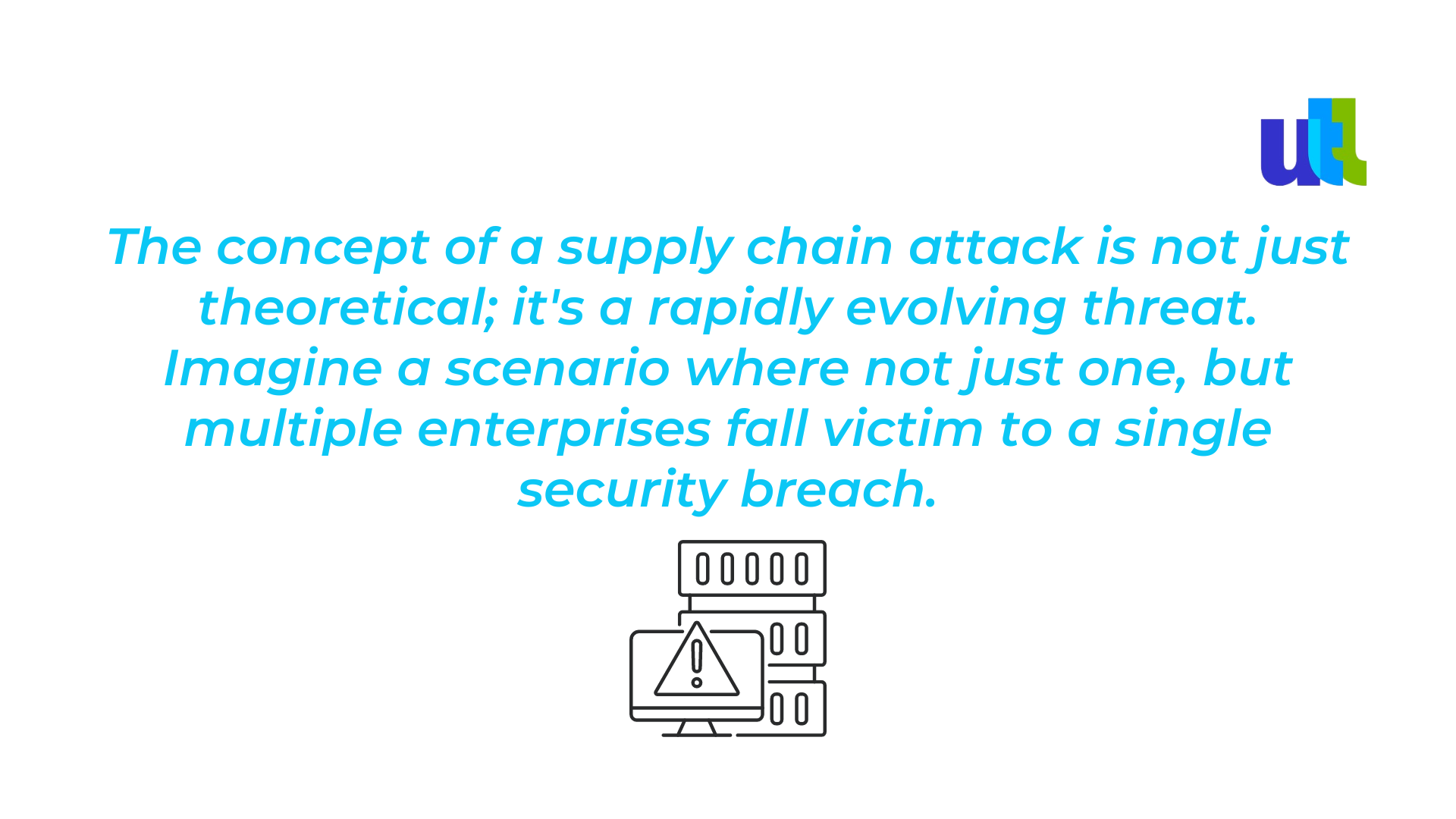
This domino effect stems from a single vulnerability in the supply chain, highlighting the concept of a supply chain attack. These attacks occur when cybercriminals exploit vulnerabilities in your supply chain network, particularly targeting vendors with less robust security measures.
Why is this form of cyberattack particularly menacing? Because it leverages the trust businesses have in their partners.

The efficiency of supply chain attacks is particularly alarming; instead of isolating their efforts on one entity, attackers compromise multiple targets through a single point of weakness.
The Anatomy of Supply Chain Attacks:
1. Software Attacks: Often, these involve manipulating a vendor's software source code, inserting malicious code into an otherwise trusted application, or even hijacking an update server to distribute malware instead of legitimate updates.
2. Hardware Attacks: These target the physical components of a network, including devices like routers, webcams, and keyboards. One common method is implanting backdoors in hardware, providing unrestricted access once the devices are deployed.
3. Firmware Attacks: Potentially the most insidious, these attacks inject malware into the boot code, allowing malicious software to activate each time the system starts. They're fast, often go unnoticed, and pose significant dangers.
Fortifying Your Digital Supply Chain: Essential Strategies

This revelation is not just a statistic; it's a clarion call for improved security postures across industries.
In the face of escalating threats, what can organizations do to shield themselves and their partners from such stealthy adversaries? Here are eleven actionable strategies:
1. Deploy Honeytokens: These digital tripwires are decoys, masquerading as valuable data. When attackers engage with them, it triggers an alert, providing organizations with precious time to counteract the intrusion and possibly even identify the source of the attack.
2. Strengthen Privileged Access Management (PAM): After an initial breach, attackers typically scout for privileged accounts to gain access to critical assets. A robust PAM framework is vital in disrupting this reconnaissance, effectively throwing a wrench in the cybercriminal's plan.
3. Adopt a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): This model dictates that no network traffic is trustworthy by default. Access is only granted after stringent verification, acting as a vigilant gatekeeper of your digital ecosystem.
4. Cultivate an 'Assume Breach' Mindset: Operate under the assumption that a breach is inevitable, propelling a proactive defense strategy across all potential attack vectors.
5. Mitigate Insider Threats: Not all security threats originate from faceless hackers. Sometimes, they're right under your roof. Regular training and a positive work culture can help prevent disgruntled employees from becoming internal adversaries.
6. Pinpoint and Shield Vulnerable Assets: Use tools like honeytokens to identify what attackers are most likely to target and fortify these assets accordingly.
7. Limit Access to Sensitive Data: Scrutinize who has access to critical information, especially among vendors. The fewer hands on it, the better.
8. Enforce Shadow IT Policies: With the rise of remote work, personal devices are more frequently used for business purposes, often without the official sanction of the IT department. Strict rules for device registration and usage are crucial.
9. Conduct Regular Third-Party Risk Assessments: Your security is only as strong as the weakest link in your supply chain. Regular evaluations help ensure that your partners are also upholding stringent security standards.
10. Monitor Vendor Networks: Continuous surveillance of third-party networks can unveil hidden vulnerabilities before they're exploited.
11. Detect and Manage Data Leaks: Stay ahead of potential breaches by identifying and managing data leaks within your vendor network. Employing managed services for this task can provide expertise and efficiency.
The Road Ahead - Cyber Resilience in the Supply Chain
The complex nature of supply chain attacks underscores their potential to cause widespread damage. These attacks aren't just about infiltrating a single company; they're about exploiting the interconnectedness of vendors, partners, and customers. The unsettling truth is that attackers don't always have to exert considerable effort in breaching highly secure networks directly. Instead, they can slip through the cracks of a third-party vendor, making their way into multiple organizations that share the same supply chain.
Statistics from reputable cybersecurity firms illustrate a concerning uptick in these incidents, with managed service providers (MSPs) being particularly susceptible. Industries like technology, financial services, and healthcare are more prone to these threats, given their extensive reliance on digital operations and sensitive data.
Given these realities, a proactive, multi-layered defense strategy is no longer optional; it's a necessity. Traditional security measures like firewalls and antivirus software, while essential, are no longer sufficient in the face of sophisticated supply chain attacks. Comprehensive risk management must be a priority, with regular assessments, robust cybersecurity protocols, and continuous vigilance as key components of an organization's defensive arsenal.
In this digital age, understanding the threats and implementing rigorous protective measures is the only way to ensure that your organization, and the countless nodes it's connected to, remains secure.
As companies increasingly digitalize their supply chains, they inadvertently expose themselves to a spectrum of cybersecurity risks. Understanding these cyber threats is the first step toward safeguarding the lifeline of your business — the supply chain.
Phishing Attacks
At the forefront of these digital assaults are phishing attacks. Here, cybercriminals hide under false identities, often using seemingly official emails to lure unsuspecting employees into a trap. These deceptive communications aim to harvest critical information such as login credentials or financial data, providing a backdoor into your network.
The Malware Attacks
Another formidable adversary is malware. This malicious software, which includes threats like viruses, ransomware, and spyware, stealthily infiltrates systems through dubious downloads, counterfeit websites, or infected devices. Once inside, it can encrypt valuable data, holding it hostage for ransom or wreaking havoc across your network and databases, ultimately aiming to pilfer sensitive information or disrupt operations.
The Enemy Within: Insider Threats
Surprisingly, not all threats originate from faceless hackers on the internet. Sometimes, they're right in your office. Disgruntled employees, or third-party vendors with access to your systems, might exploit their positions, stealing intellectual property or other confidential data for personal gain or out of malice.
The Weak Link. Third-Party Security Risks
In our interconnected commercial environment, a company's cybersecurity posture isn't just about its own practices; it's also as robust as the weakest link in its chain. Third-party vendors, essential for functions like logistics and warehousing, can become liabilities if their cybersecurity measures are lax. A breach in their systems can easily become a breach in yours.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APT)
Among the most insidious of attacks are Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). These long-term assaults are orchestrated by highly skilled cybercriminals who infiltrate a network and lie dormant, sometimes for months, avoiding detection while continuously mining data or preparing for a larger, coordinated strike.
The IoT Imperative: New Devices, New Vulnerabilities
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized supply chain management with devices like wireless sensors and smart security systems. However, when these IoT devices are inadequately secured, they serve as perfect entry points for attackers to breach your network.
Cryptojacking
A more recent phenomenon in the threat landscape is cryptojacking, where hackers hijack your company's devices to mine cryptocurrency. This covert operation significantly drains system resources, impeding the performance of crucial supply chain operations.
Social Engineering
Social engineering attacks manipulate employees into relinquishing sensitive information. By employing various deceptive tactics, cybercriminals can acquire high-profile employees' credentials, easing their unauthorized entry into secure networks.
Data Breaches
Whether through sophisticated cyber-attacks or mere employee negligence, data breaches spell disaster for any company. The unauthorized exposure or theft of customer data, financial details, or trade secrets can tarnish a company's reputation and have far-reaching financial implications.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks aren't about theft; they're about disruption. By overwhelming your systems with a flood of bogus traffic, attackers can paralyze your operations, causing significant downtime and financial loss.
Cloud Security Risks
The migration to cloud-based platforms, while a boon for digital transformation, comes with its own set of vulnerabilities. Issues like unauthorized access and misconfiguration can pose serious threats to the data integrity and security of companies leveraging the cloud for their supply chain operations.
Accidental Exposure
Sometimes, cyber breaches are born from simple human error. A misdirected email, an incorrect data input, or misconfigured settings can inadvertently expose critical company data to unauthorized individuals.
Evolving Strategies in Cybersecurity Supply Chain Risk Management
As we gaze into the future, several trends are set to shape the cybersecurity supply chain risk management landscape. An amplified emphasis on third-party risk management, the leveraging of AI and machine learning for enhanced security protocols, increased adoption of blockchain for improved transparency, and more stringent regulations are on the horizon.
Innovations will continue to alter the threatscape, necessitating that organizations remain vigilant in updating their cybersecurity strategies. By proactively adapting to these evolving dynamics, companies can fortify their supply chains against the ever-present cyber threats, safeguarding their operations and maintaining their competitive edge.
In conclusion, the digital age, with all its benefits, brings with it the unavoidable reality of cyber threats. For businesses deeply intertwined with technology, especially in their supply chains, vigilance, comprehensive cybersecurity measures, and a forward-thinking approach are their best defenses against this pervasive digital menace.
For free consultation on preventing supply chain cyberattacks, click here.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
View the full presentation:
WRITTEN BY
Milda Butkeviciute
2023-10-18